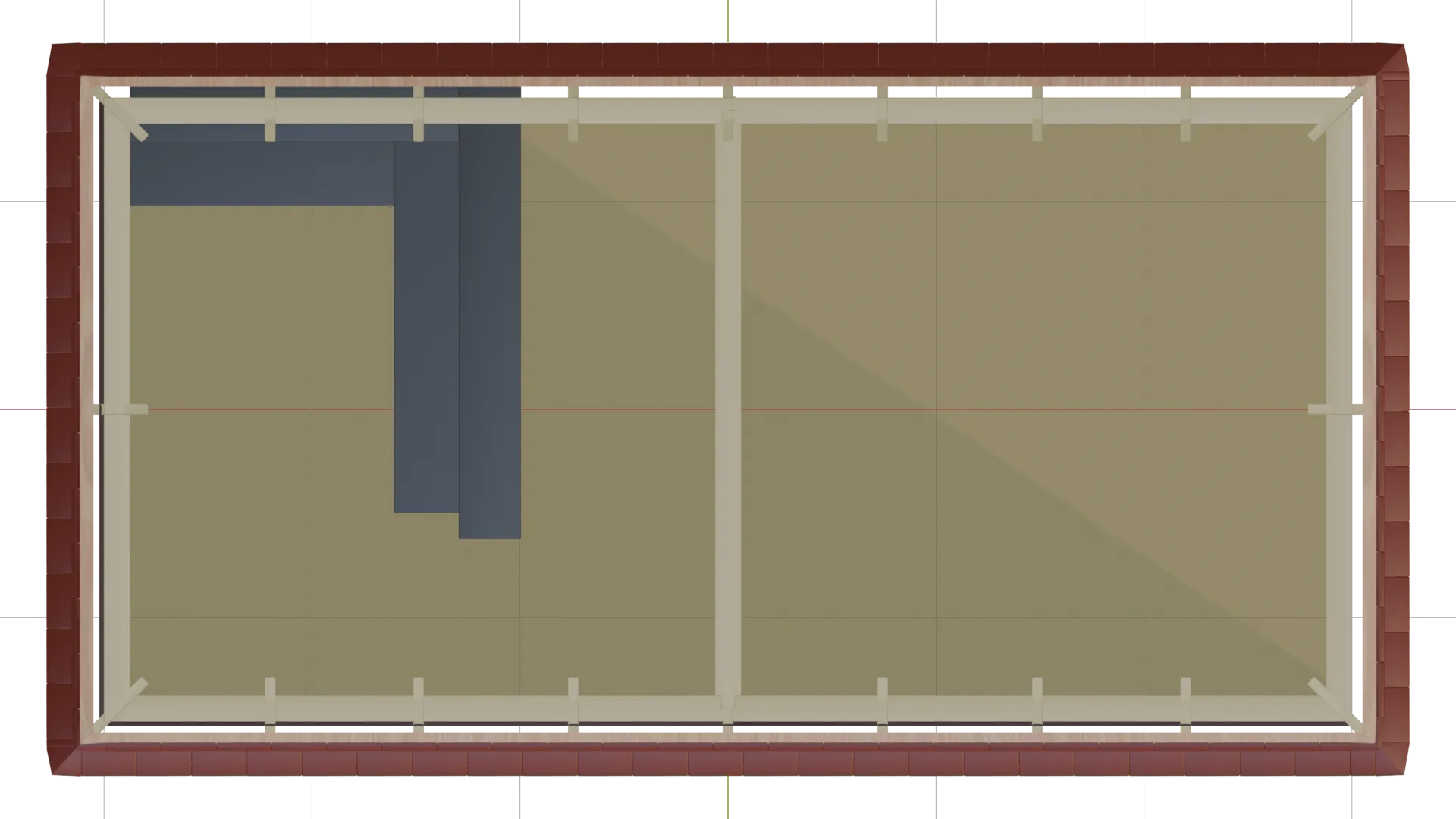
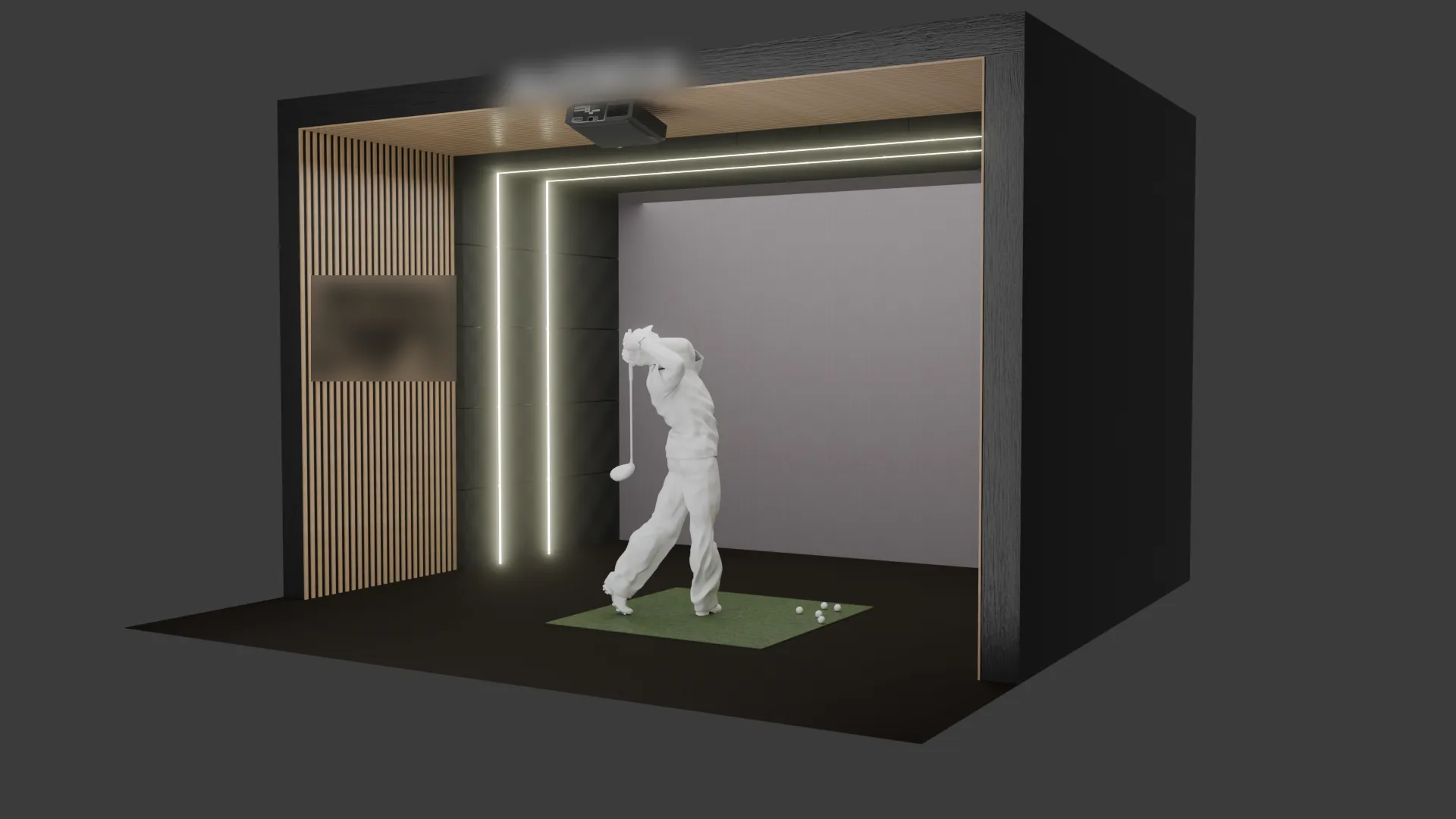
Bespoke Golf Simulator (2025)
This interior golf simulator was developed as a bespoke visualisation, with close attention paid
to spatial accuracy, material realism, and lighting atmosphere. The scene was built in Blender
using an efficient, non-destructive workflow—leveraging array modifiers for structural
repetition and bevel modifiers to introduce subtle edge highlights and a polished finish.
Materials were sourced and refined using BlenderKit, with careful UV mapping applied across all
assets to ensure correct texture scale and orientation, particularly for wood grain and panel
detailing. Lighting was approached both functionally and aesthetically, with LED strip
illumination enhanced using fog glow to achieve a soft, ambient spill that reflects real-world
architectural lighting conditions.
Rendering was completed in Cycles to maintain physically accurate light behaviour and surface
response. Secondary assets such as the projector and golfer were integrated from external model
libraries to support the overall narrative of the space. Throughout the process, material
selections and visual direction were refined collaboratively to align with the intended use of
the simulator and the client's expectations, resulting in a clean, realistic representation.


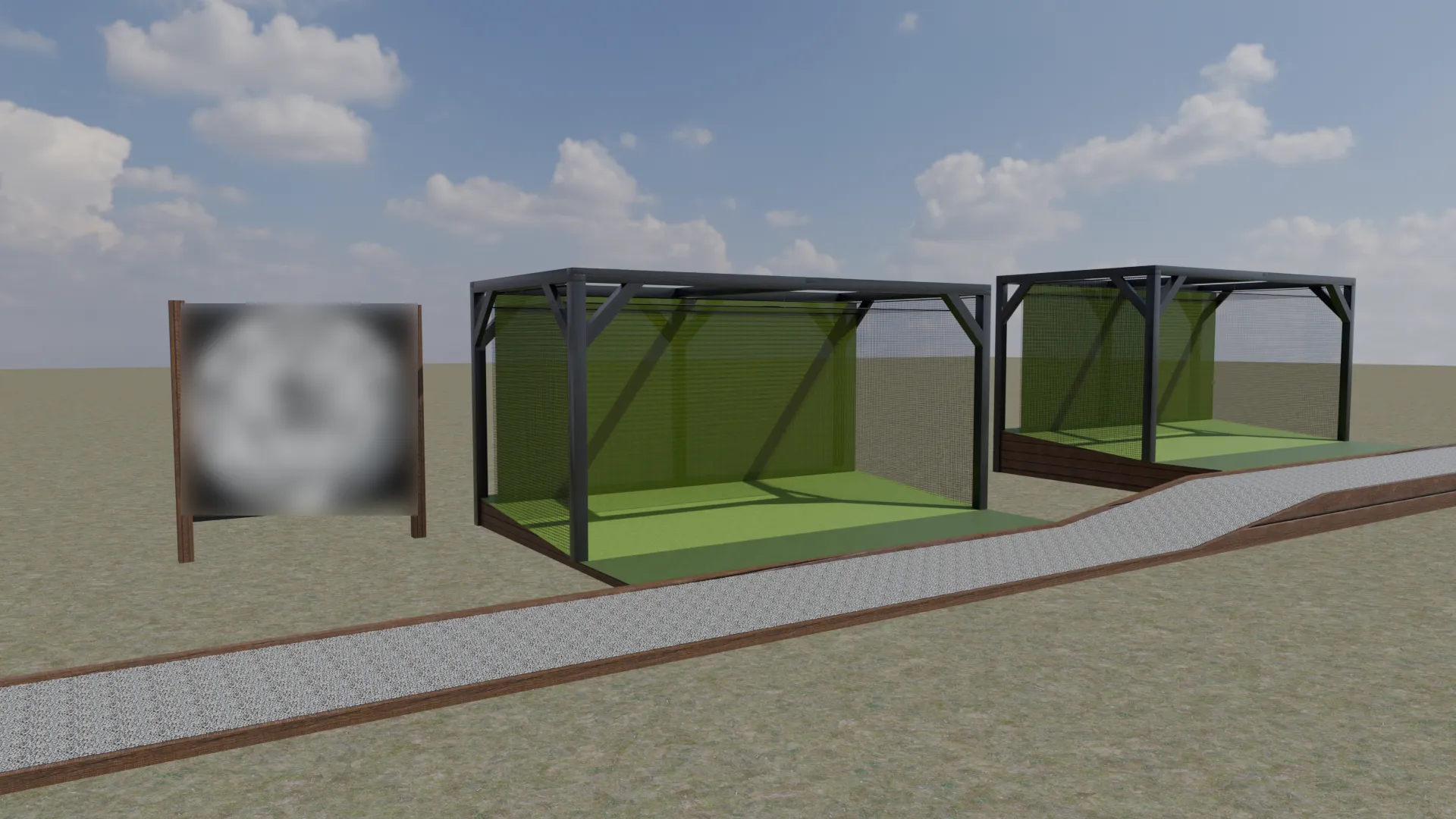
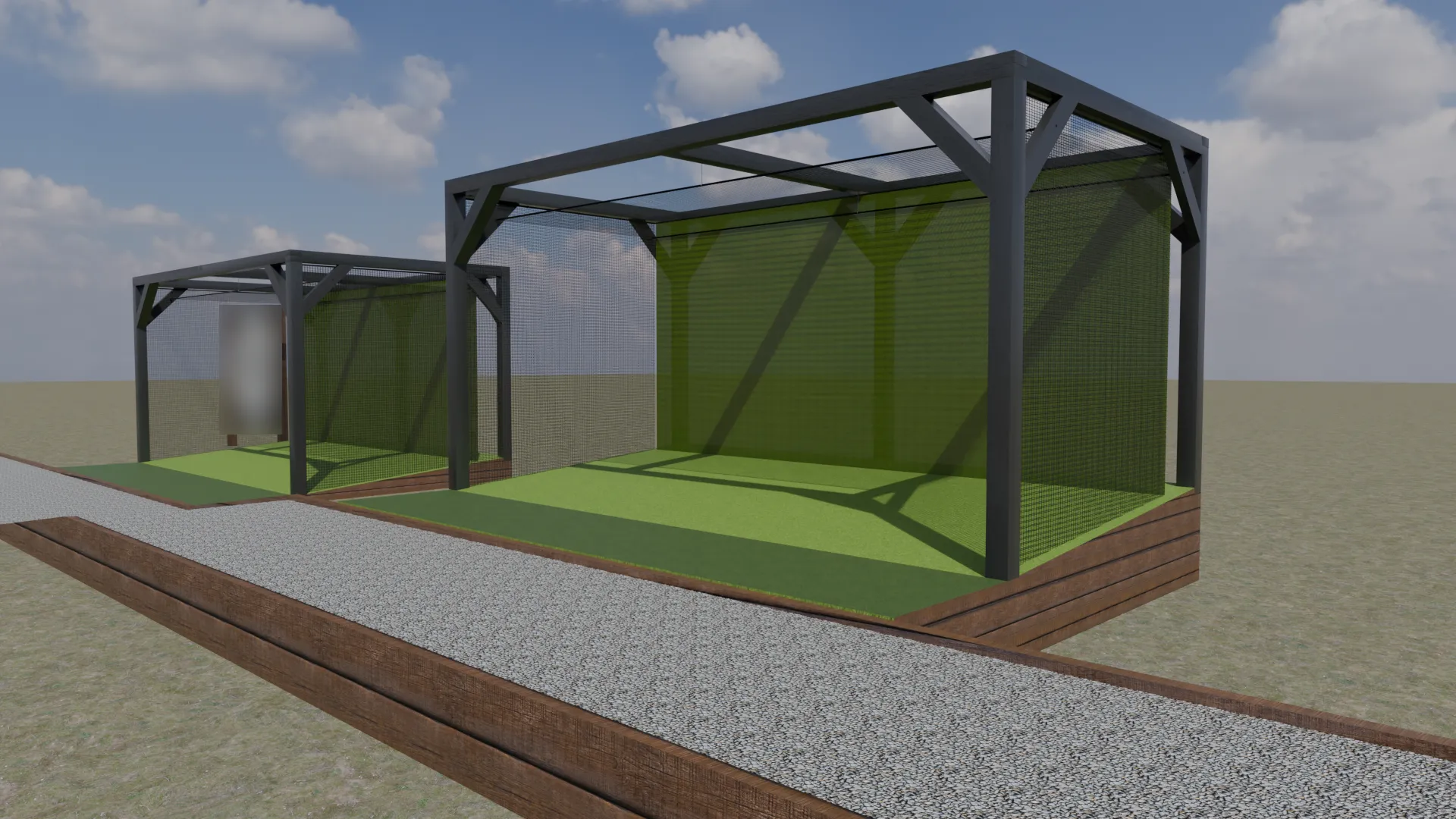
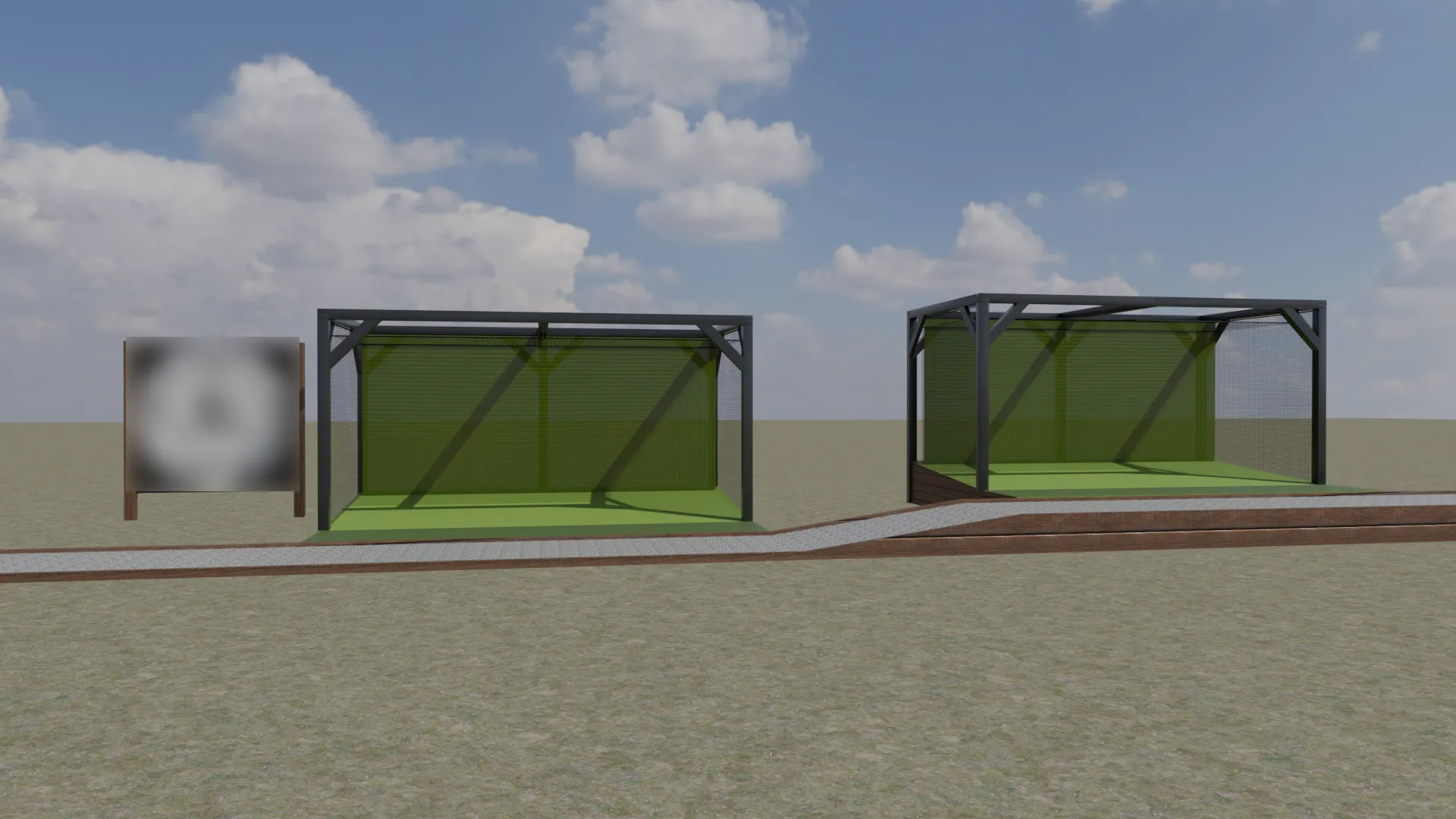
Outside Golf Simulator (2025)
This outdoor golf simulator concept was developed as a clear, functional visualisation to
communicate layout, scale, and material intent with minimal complexity. The structure was
modelled in Blender using an efficient modifier-based workflow, combining array and bevel
modifiers to quickly establish a clean, repeatable wooden frame with subtle edge refinement.
Materials were sourced and adjusted via BlenderKit, with selections aligned
collaboratively.
The enclosure system was intentionally kept lightweight, using simple planes with tailored
materials to represent the primary hitting net and secondary ball-capture netting. This approach
allowed the focus to remain on proportion, usability, and overall concept clarity, while
enabling the entire scene to be assembled and rendered in a very short timeframe.


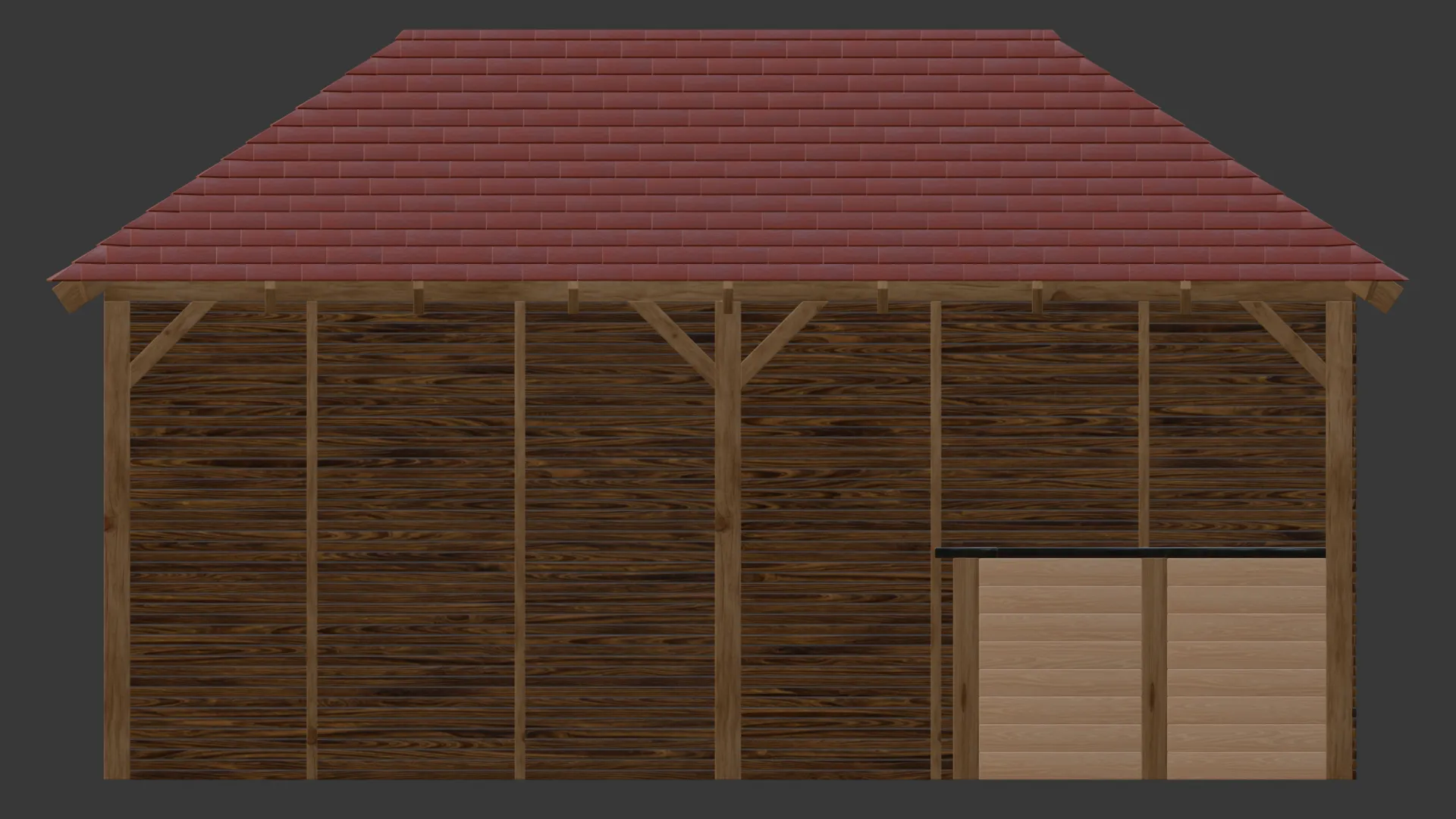
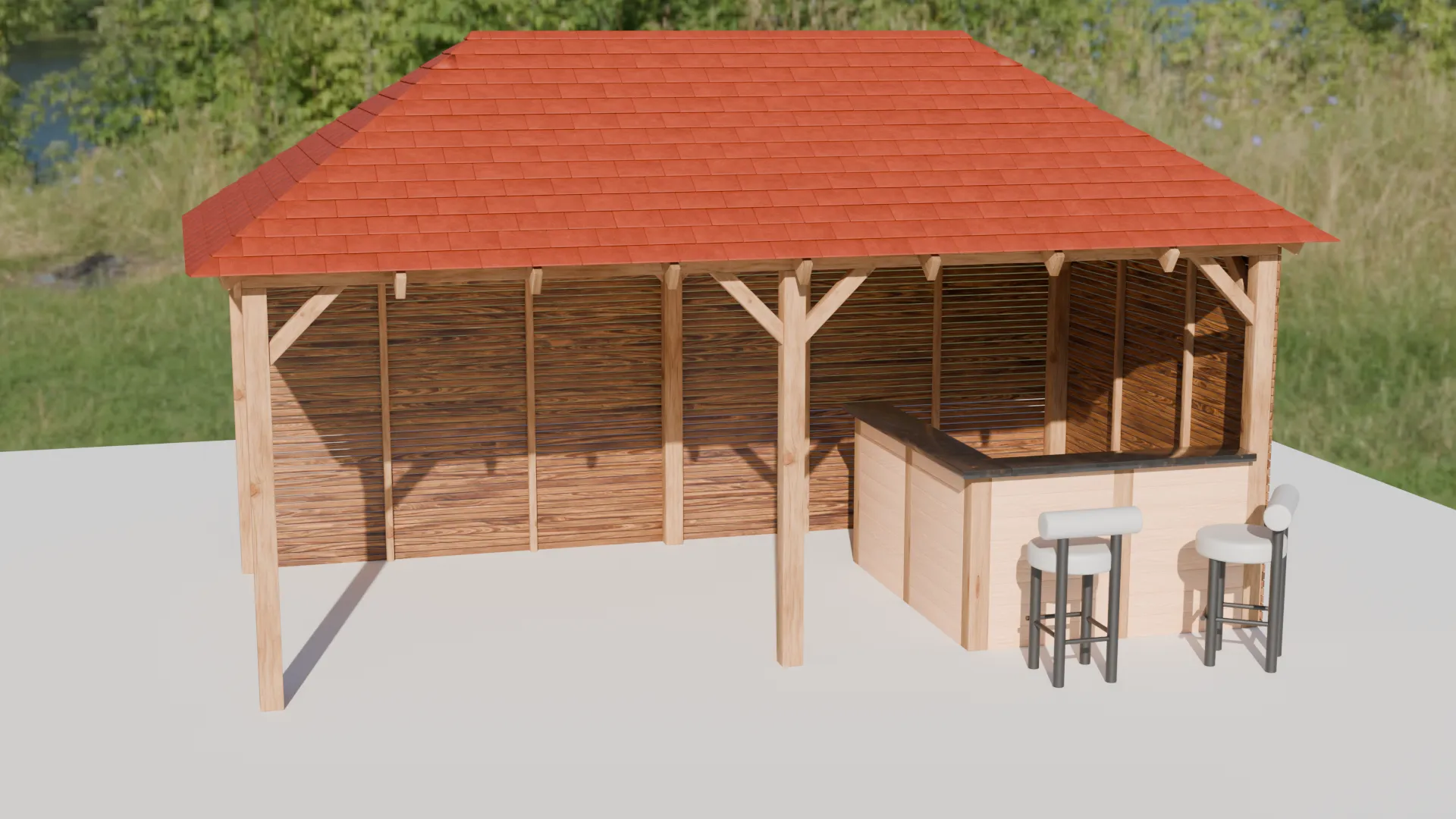
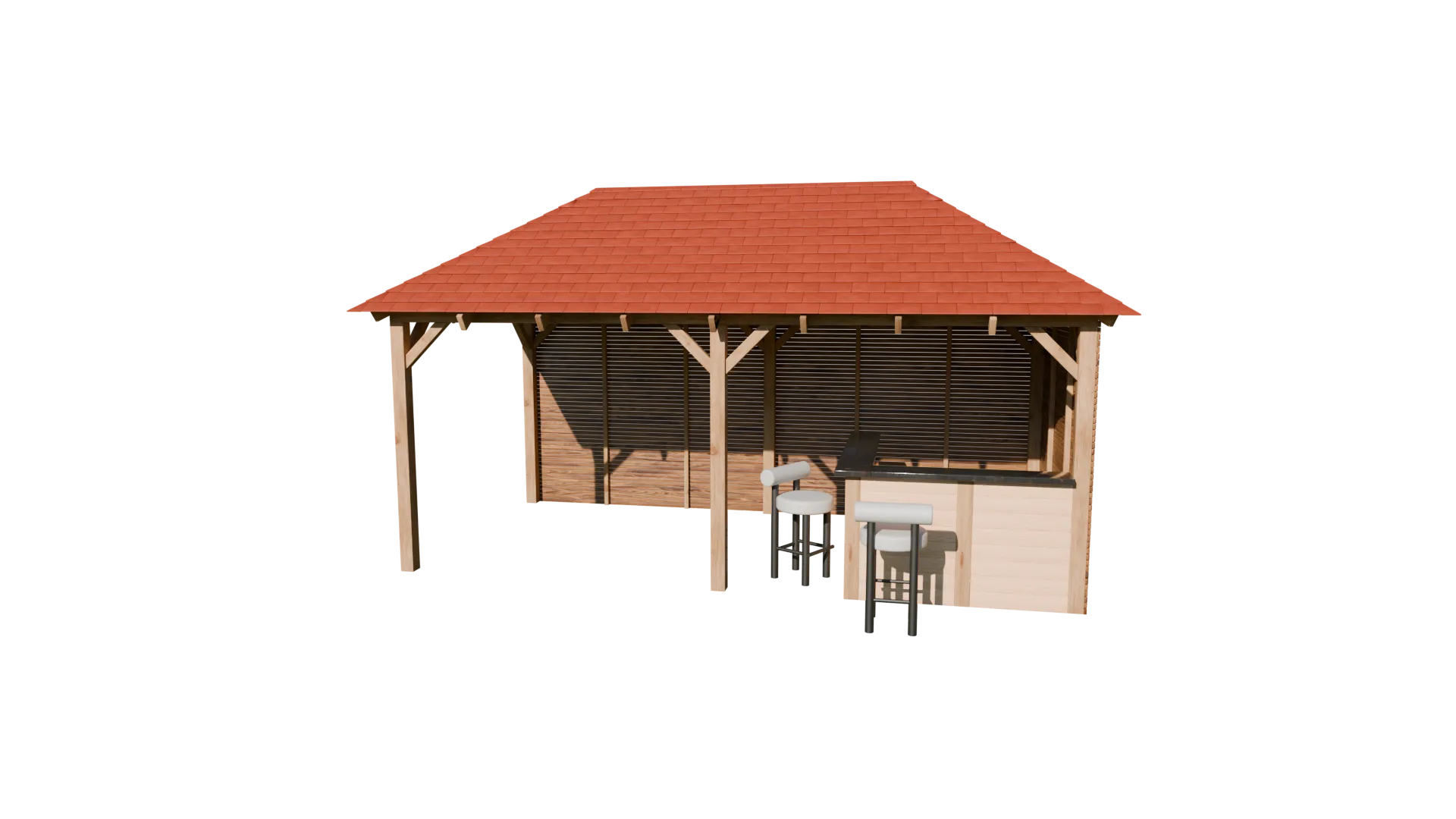
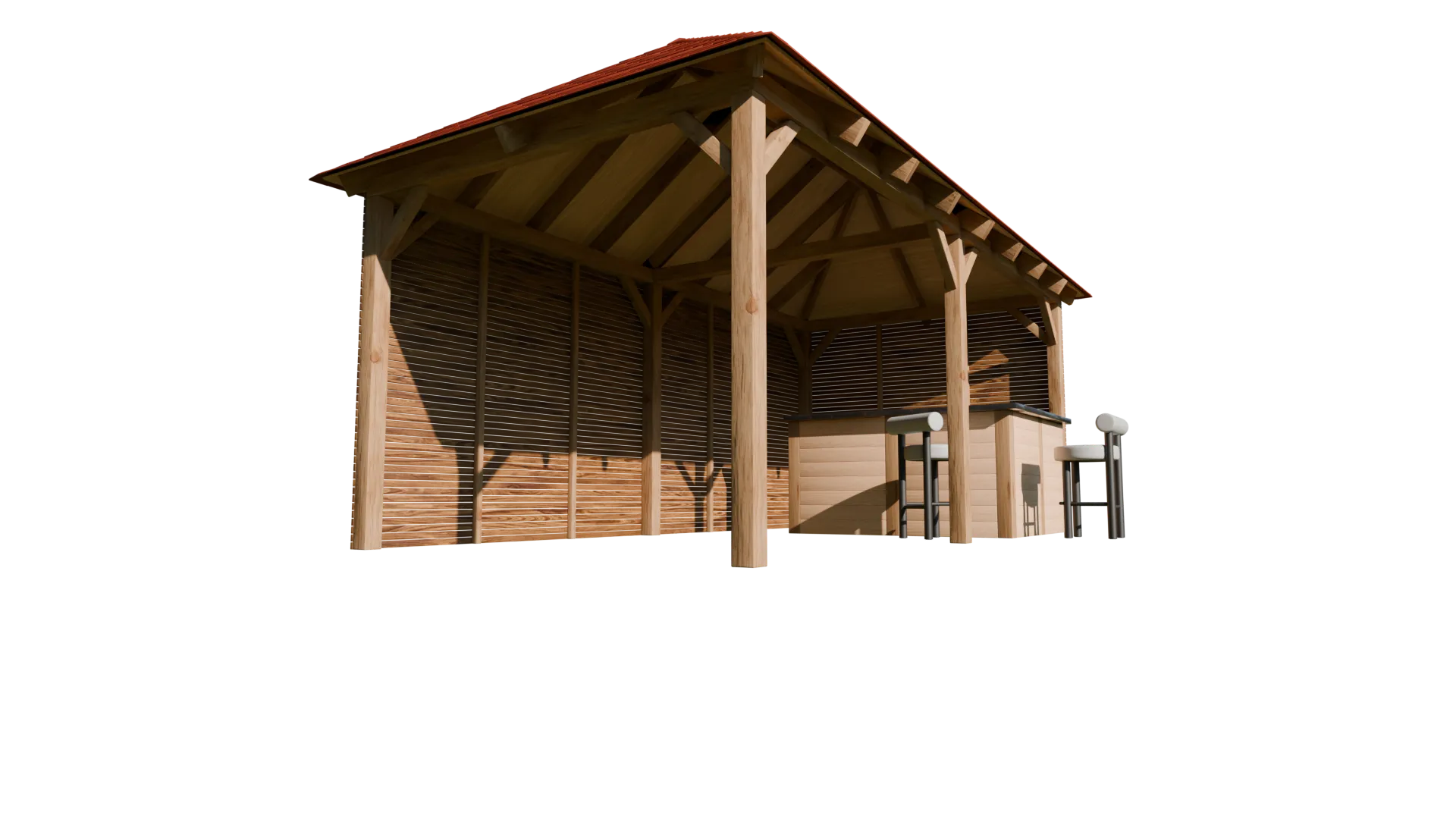
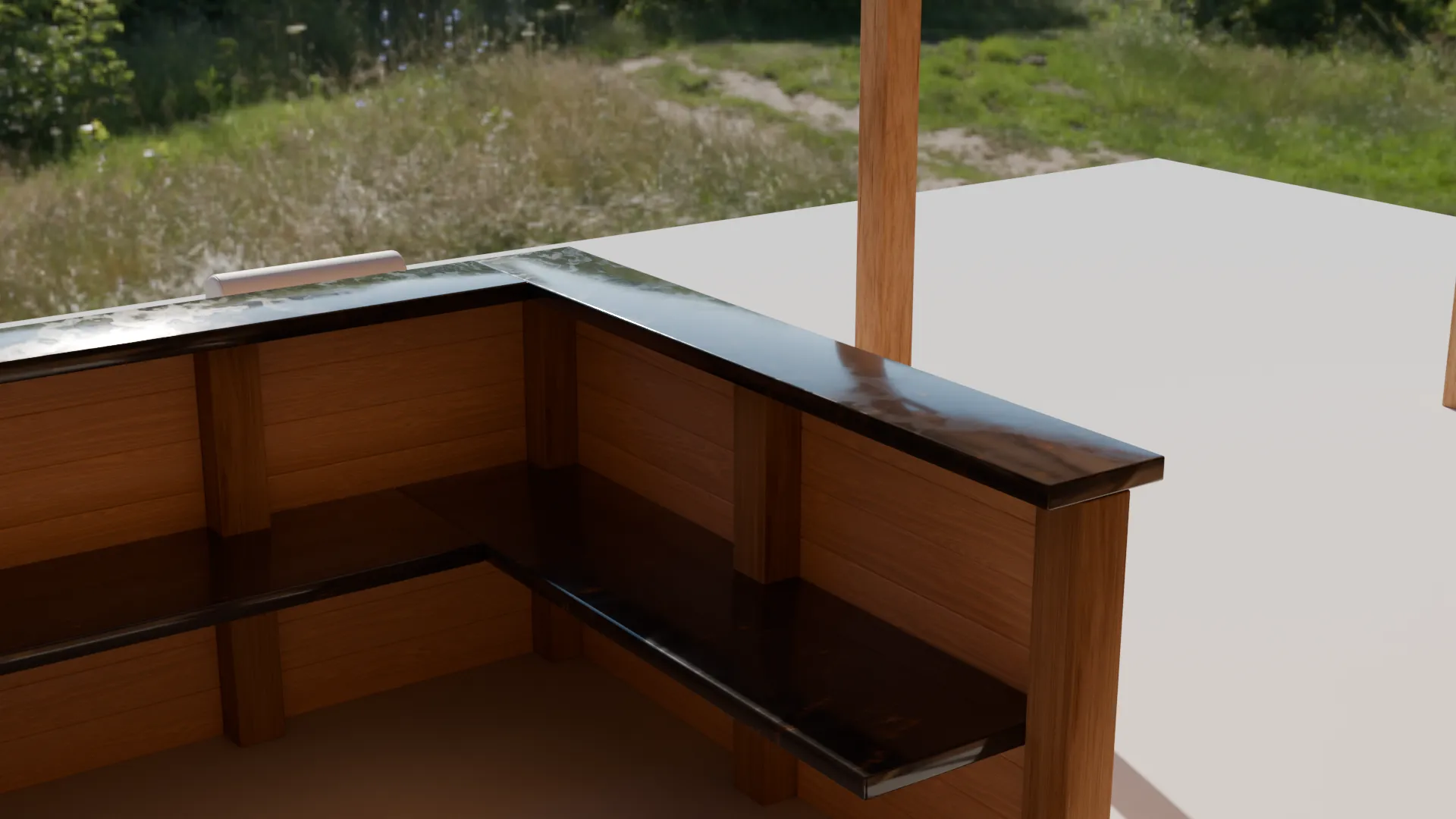
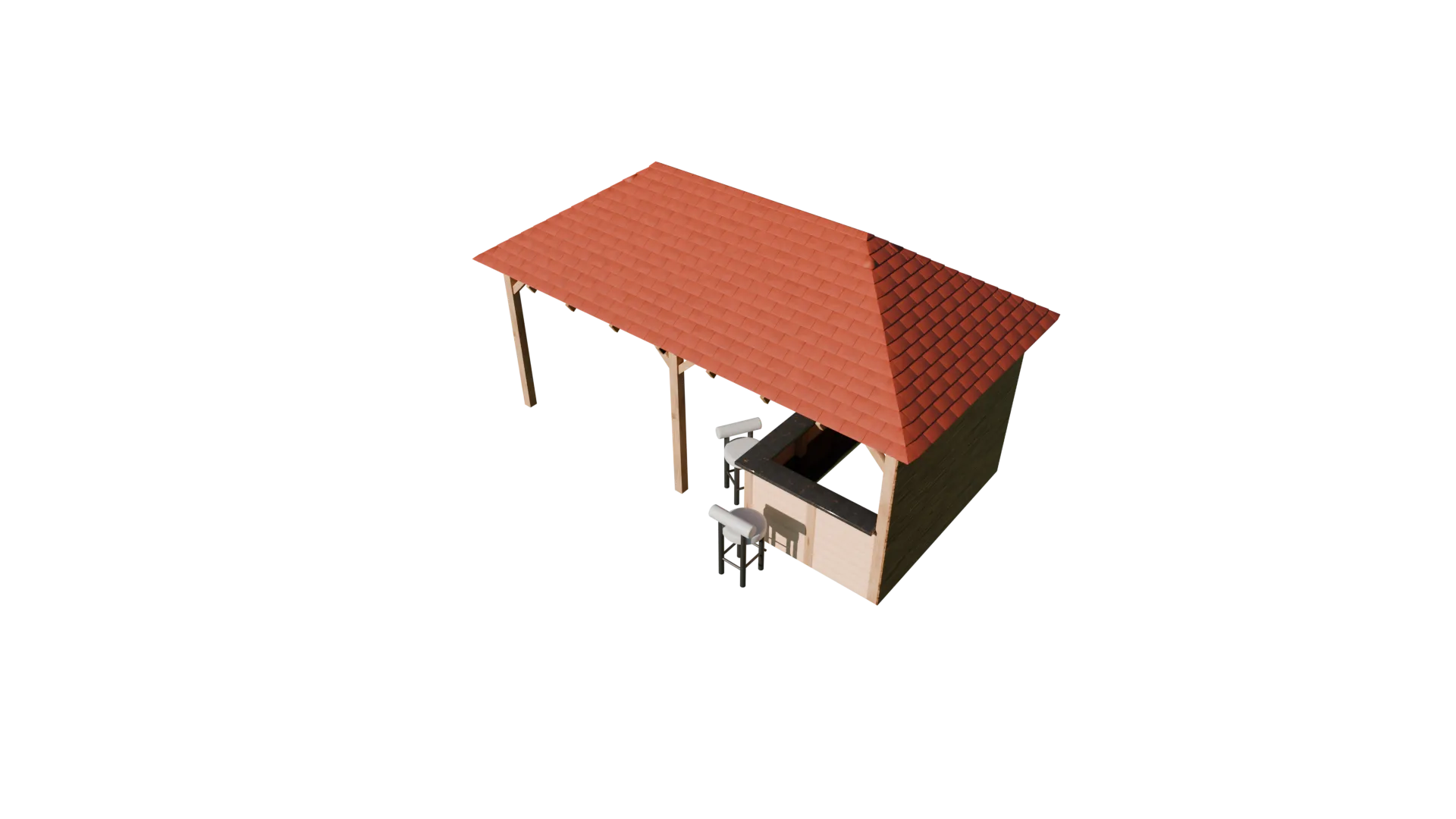
Outside Bar (2025)
This outdoor bar structure was developed as a practical visualisation to support early design
decisions, with close attention given to overall dimensions, proportions, and material intent
agreed during initial discussions. The model was produced in Blender using a clean,
modifier-based workflow, with array and bevel modifiers forming the basis of the timber frame
and structural detailing. Materials were sourced and refined using BlenderKit to achieve a
natural, realistic finish, while the roof tiles were constructed using array modifiers to create
consistent spacing and repetition across the pitched roof.
During development, the bar layout was revised in response to client feedback, with the counter
depth reduced from extending halfway towards the central post to occupying approximately one
third of the internal space. Because the structure was built using non-destructive array
workflows, this adjustment was implemented quickly and accurately without compromising the
overall design. Seating elements were integrated using externally sourced models to complete the
scene, resulting in a clear, construction-aware visual suitable for design review and
presentation.